Introduction:
In recent years, many technologies have been introduced. These technologies have played a great role in changing business operation processes and disrupted many industries. Among many advancements, AI stands out as a major key player. It refers to computer intelligence in which machines mimic human intelligence to solve problems, predict outcomes, and make decisions. However, business intelligence (BI) is the backbone of data-driven decision-making. It helps businesses to collect, analyze, and visualize data to act with speed. Furthermore, businesses explored new ways to streamline operations and the synergy between AI and BI has led to the development of RPA. RPA stands for Robotic Process Automation. Where AI bring intelligent automation, BI delivers actionable insights to businesses and RPA is a solution for SMBs to eliminate repetitive tasks.
In this blog, you will learn what is artificial intelligence, business intelligence and robotic process automation. Moreover, you will find out the key differences between AI and BI and how businesses can harness their combined power for success.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
In computer science, Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to making machines think, learn, and solve problems like human intelligence. It works by using data and past experiences(training) to make decisions, predict outcomes, and improve over time. However, It includes several core areas:
The first core area is machine learning which helps computers make data analysis by recognizing patterns and making predictions. Then comes, neural networks which work as a brain to solve complex problems through interconnected processing units. Furthermore, Natural Language Processing (NLP) let machines understand and interpret human language for applications like chatbots and document analysis. Lastly, Robotics. They focus on building machines that can perform tasks autonomously. Together, all these elements make artificial intelligence a backbone for industries in enhancing efficiency and solving real challenges.
→ For example: in healthcare, IBM Watson Health provide AI-powered tools that help analyze patient data. This data helps doctors diagnose diseases accurately and faster than ever.
What is Business Intelligence (BI)?
Business Intelligence (BI) is a technological process that involves collecting, analyzing, and presenting data. This process helps businesses make smarter decisions. It works by turning raw data to use for analyzing trends and patterns. It visualizes data from dashboards, charts, or reports for easy interpretation. BI tools help leaders to get opportunities, address challenges, and plan strategically. BI includes several key components including:
All these elements make BI for businesses strive to optimize processes and they can respond proactively to market demands.
→ For example: In retail, Tableau a company uses BI tools to analyze customer behavior. It helps them forecast demand, manage inventory, and improve marketing strategies.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic process automation in businesses uses software robots to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks. Bots mimic human actions to enter data, process transactions, make Excel sheets or respond to customer queries. The process is faster with bots and it is done without errors. There is no need when using RPA to change existing systems. This factor makes RPA a cost-effective solution to streamline workflows. For example:
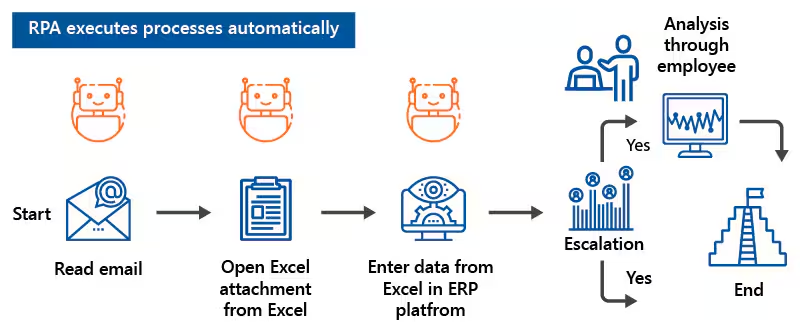
An RPA bot can automatically read emails, extract data from an Excel attachment, and input that data into an ERP platform. However, if the process requires further review or escalation. RPA notifies a human employee for analysis. As a result, there is a smooth and efficient workflow and minimizes manual effort while maintaining accuracy.
→ For example: RPA in finance helps automate invoice processing and reconcile transactions, reduce manual effort and ensure accuracy.
AI vs BI vs RPA- Fight of Brains
AI, BI and RPA are tools that can often overlap in their applications, their purposes, approaches, and capabilities are distinctly different. Businesses should know how they complement each other, their goals, benefits, use cases and key differences to utilize these technologies at their best. Let’s start:
The Goals Of AI, BI and RPA
AI: Artificial Intelligence’s key goal is to bring automation in processes like decision-making, problem-solving, and predictive analysis. For example, AI can provide personalized medical advice in healthcare through chatbots and predictive models.
→ Do you know?
AI’s strength lies in its ability to learn and improve over time which means, it is ideal for data-rich environments.
BI: On the other hand, Business Intelligence (BI) does not make decisions or predictions. Instead, it provides clarity and insights based on historical and real-time data like BI tools like Power BI create dashboards to help businesses track sales, monitor KPIs, and identify trends. According to CIO Magazine Article, Business Intelligence doesn’t tell you what to do; it tells you what was and what is.”
→ Do you know?
BI’s strength lies in its ability to empower decision-makers with the information they need to act effectively and quickly.
RPA: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a different technology from AI and BI. It automates tasks that do not require human judgment. RPA bots can replicate human actions to enter data into systems and tasks like generating reports. An RPA bot can do tasks like read emails, extract data from attachments, and upload the information to an enterprise system. As a result, it frees up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
→ Do you know?
RPA excels in improving operational efficiency without requiring changes to existing systems.
Benefits of AI, BI and RPA
This trifecta of technologies offers unique advantages to businesses which helps them to operate effectively and competitively. Let’s check some benefits of each technology:
Advantages of AI
- Automated Decision-Making: AI analyzes large datasets in real-time which helps it make complex decisions. An example is AI in finance, AI can assess loan applications by evaluating credit scores, income, and spending habits. As a result, AI reduces human bias and speeds up approvals.
- Predictive Insights: AI in businesses can predict upcoming trends and behaviors. For example, AI in Retail can predict customer demands which is best for better inventory management and reducing waste.
- Personalization: AI can have individual preferences. Based on it, AI can tailor user experiences. For example, Netflix and Spotify use AI to recommend content users are likely to enjoy. As a result, AI in entertainment enhances customer satisfaction and retention.
- Fraud Detection: AI in banking can help in monitoring transactions. It can also identify anomalies that signal potential fraud. AI systems can adapt to emerging patterns and offer robust security.
- Learning and Adaptation: Static systems require information again and again. However, AI trains with new data. It refines its output over time which makes it ideal for industries like healthcare, where patient outcomes and diagnostic accuracy matter.
Advantages of BI
- Decision-Making: Business intelligence changes new data into meaningful insights. It presents data in the form of dashboards, charts and graphs. As an example, AI in sales can help teams track performance metrics so they can adjust strategies to meet targets more effectively.
- Customer Behavior Analysis: When businesses use BI tools, they collect data from various customer touchpoints, such as social media, email, and website interactions. BI provides a unified view to businesses which helps them understand customer needs, preferences, and pain points for more targeted marketing campaigns.
- Performance Monitoring: Every business needs updates like KPIs for performance marketing. BI tools provide real-time updates on KPIs to help businesses identify drawbacks. For example, logistics companies utilize BI tools to monitor delivery times and optimize routes.
- Strategic Planning: The key feature of BI is being able to provide current and past insights that can support leaders with long-term strategic planning. For instance, BI in businesses can analyze market trends to help them position themselves effectively for future growth.
- Cost Optimization: BI uncovers areas of inefficiency in advance. Hence, businesses reduce operational costs by identifying underperforming products or redundant processes that could lead to significant savings.
RPA Benefits
- Efficiency: RPA bots can work 24/7. They can cover high-volume tasks like payroll management at speeds that a human cannot do. The speed can boost productivity and free up employees for higher-value work.
- Error Reduction: RPA automates tasks and eliminates human error. For example, RPA for manual data entry provides greater accuracy. In addition, RPA in healthcare reduces billing errors by standardizing processes.
- Cost Savings: Repetitive tasks give rise to errors when done by humans. That is why automating repetitive tasks boosts productivity, and reduces labor and operational costs. As an example, if RPA is used in banks for loan processing, it can handle more applications with fewer resources.
- Scalability: Robotic Process Automation scales operations up or down quickly based on business needs. It means RPA in e-commerce can help in peak seasons. Deploying additional bots can handle increased order volumes without hiring temporary staff.
- Seamless Integration: RPA does not need new systems they can be integrated with existing ones to automate tasks. For example. RPA in HR can extract employee data from legacy systems and update records in modern applications.
AI vs BI vs RPA – Use Cases
Artificial and business intelligence and RPA provide unique capabilities to transform businesses. Let’s explore the use cases of each technology in detail to know their differences in detail:
Use Cases of AI
- Fraud Detection: AI in finance can monitor transactions in real-time. It can detect anomalies, identify potential fraud, and flag suspicious activities. AI in finance can analyze large datasets. This information helps AI to recognize patterns that indicate fraudulent behavior. For instance, PayPal uses AI algorithms to safeguard user accounts and transactions.
- Personalization Engines: Amazon and Netflix use AI to provide personalized recommendations that are accurate to customer behavior, browsing history, and purchase patterns. AI in entertainment analyzes data to predict what a user might like. It can improve the overall customer experience and boost sales.
- Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing: Machinery often fails to predict and analyze sensor data. But, AI predicts even hidden data which prevents costly downtime. In addition, AI in manufacturing can help monitor equipment performance and alert operators when maintenance is required. As a result, AI can ensure smooth operations and cost savings.
BI Use Cases
- Dashboards: BI tools help businesses get insights by providing real-time dashboards. These dashboards can help them track sales across different channels. If businesses integrate BI, they can monitor performance, identify underperforming products, and adjust strategies on the go resulting in informed decisions.
- Marketing Campaign Performance: BI in Marketing teams can help measure campaign status, and how successful they can be. BI analyze metrics like click-through rates, conversions, and ROI. Thus, the collected data helps marketers optimize future campaigns for better allocation of marketing budgets.
- Identifying Customer Trends and Patterns: BI in businesses can reveal trends like which products are most popular in certain regions. Business intelligence can help many domains in tailoring their inventory and promotions accordingly.
RPA Use Cases
- Automating Invoice Processing: RPA in accounting provides bots that extract data from invoices, validate it, and input it into accounting software. Imagine a finance department using RPA and streamlining hundreds of invoices daily with reduced errors and processing time.
- Managing Employee Onboarding: RPA in HR can automate tasks that are repetitive like generating offer letters, collecting employee documents, and entering data into HR systems. AI and RPA provide a faster onboarding process while reducing manual effort.
- Handling Customer Inquiries: In the customer support domain, customers get frustrated if do not get quick responses, leading to a loss of customers. When customer support gets RPA-powered chatbots integrated, they reduce wait times and increase accuracy rates. RPA bots can answer frequently asked questions, route complex inquiries to human agents, and log interactions in CRM systems.
AI vs BI vs RPA: Key Differences
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Business Intelligence (BI), and Robotic Process Automation (RPA), each have unique purposes within a business. For example:
AI enable machines to learn, adapt, and make predictions or decisions autonomously. BI centers around analyzing historical and real-time data to provide actionable insights for better decision-making. In contrast, RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks by replicating human actions in data entry or invoice processing. Each helps businesses in distinct ways as AI excels in fraud detection, customer personalization, and predictive maintenance. However, BI simplifies complex datasets by providing dashboards, charts, and reports to help businesses track trends, monitor KPIs, and plan strategically. Moreover, RPA takes this further by enhancing efficiency by eliminating manual tasks. Together, they complement each other and create a seamless data-driven business ecosystem. Let’s compare in a table:
Table: Comparison of Differences Between AI, BI and RPA
| Feature | AI | BI | RPA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | AI mimics human intelligence to solve problems, learn, and make decisions. | BI focuses on collecting, analyzing, and visualizing data for decision-making. | RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks using bots. |
| Goal | To enable machines to think, predict, and adapt autonomously. | To provide actionable insights and support strategic planning. | To improve operational efficiency by eliminating manual tasks. |
| Function | Predictive analytics, decision-making, and process automation. | Data aggregation, trend analysis, and visualization. | Automating repetitive workflows and reducing manual errors. |
| Technology | Machine learning, neural networks, NLP, robotics. | Dashboards, reporting tools, data warehousing. | Software bots, scripts, and workflows. |
| Approach | Adaptive and self-learning systems. | Retrospective and real-time data analysis. | Rule-based automation without self-learning. |
| Use Case | Fraud detection, customer personalization, predictive maintenance. | Sales tracking, marketing performance analysis, and customer behavior analysis. | Invoice processing, onboarding, and customer query handling. |
| Strengths | Learns and improves over time; excels in dynamic environments. | Simplifies data interpretation; drives data-informed decisions. | Fast execution of tasks; eliminates errors in repetitive processes. |
| Limitations | Requires significant computational power and data. | Does not provide predictive or prescriptive insights. | Limited to rule-based tasks and lacks decision-making capabilities. |
| Integrations | Enhances BI and RPA with predictive and prescriptive capabilities. | Provides foundational insights for AI and RPA automation. | Automates BI workflows and executes tasks based on AI insights. |
| Best-suited | Complex, data-rich tasks requiring prediction and adaptability. | Visualizing trends, analyzing historical data, and planning. | High-volume, repetitive tasks across various departments. |
How AI, BI, and RPA Work Together
While being distinct technology, AI, BI and RPA are highly complementary technologies. When BI organizes and visualizes data, RPA automates repetitive workflows, and AI brings intelligence and adaptability to the mix. It indicates that together they can create a powerful ecosystem which can enhance efficiency and decision-making. For example: BI in retail can analyze customer purchasing patterns, while RPA in inventory management brings automation based on BI insights. Further, AI can predict future demands and suggest personalized marketing campaigns. Hence, the synergy of these technologies makes businesses act proactively to stay competitive.
Choose the Right Technology
Businesses can select between Artificial Intelligence (AI), Business Intelligence (BI), and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) but before that, they need a clear understanding of business needs and goals. They should know how each technology has unique strengths and how they are suited for specific tasks. It is important to know how they also complement one another to create an efficient and innovative ecosystem. Here’s a breakdown of when to use each:
- Use Business Intelligence (BI) if you want to analyze historical data, identify trends, and support strategic planning. It can help organizations make data-driven decisions. BI is ideal for tracking performance, identifying trends and strategic planning. According to Gartner, 30% of enterprises have adopted BI. Moreover, the business intelligence (BI) market is expected to reach $116.25 billion by 2033.
- Use RPA when there is a need for automation for manual, repetitive, rule-based tasks. It can reduce human effort, and errors and ultimately increase productivity without requiring major changes in existing systems. RPA is best suited for customer support HR processes and anything that requires automation. According to Gartner, the RPA market grew to $3.2 billion, a 22.1% increase from 2022 to 2032.
- Use AI when businesses need predictive analysis to make decisions. AI in business can handle data-intensive processes and train over time with machine learning. AI excels in tasks like fraud detection and disease diagnosis.
Innovate Your Business With RPA Integration
http://optimusfox.com is an AI development company that focuses on solving current challenges by transforming businesses through cutting-edge technologies. With years of excellence in providing AI development services, RPA integration and custom data-driven solutions, our team excels in navigating business challenges in the first call. Collecting the information, we strategize and craft solutions to empower your businesses to thrive in competitive markets. If your business struggles with repetitive, time-consuming tasks that slow down operations and reduce productivity. Get RPA solutions to eliminate inefficiencies and focus on growth.
Conclusion
It is not about which technology you choose. It is important to align them with your business needs and get maximum potential. Whether you choose one or three for integration, each will help you create a robust framework for your business. Ultimately, this integration will streamline business operations, enhance decision-making, and put you on the edge of competitive markets.
Integrate AI, BI, or RPA And Turn Challenges Into Opportunities!





