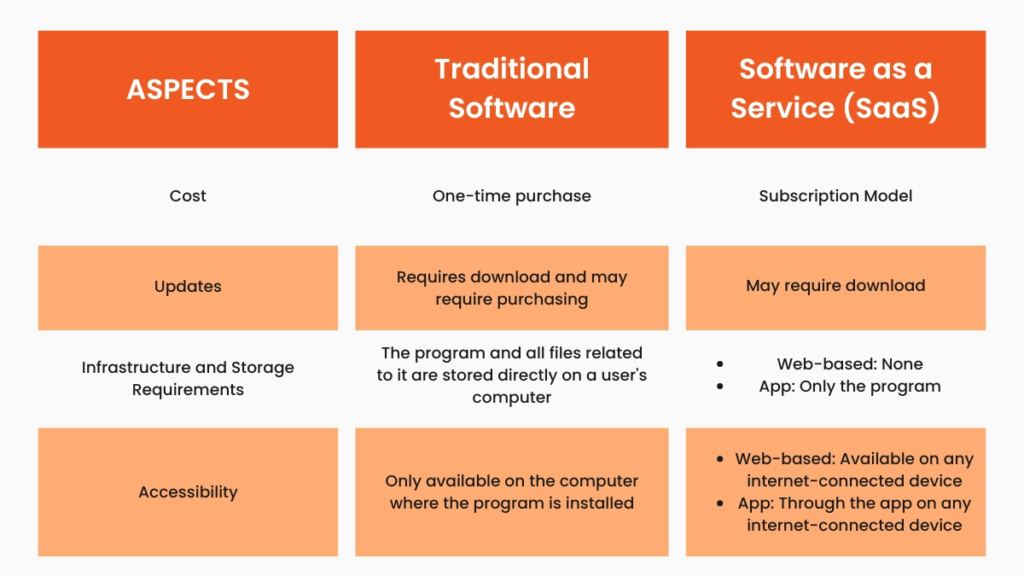
Traditionally, software was primarily delivered and deployed through a software licensing model. Businesses and individuals had to buy software licenses like CDs, and floppy disks or install the software in their local machines or servers. The major drawback of this process was that users had to pay a large amount for the software upfront rather than on a subscription. This model is known as on-premises software. Moreover, businesses had to maintain dedicated infrastructure (servers, networks, etc.) to support the software. This maintenance is costly and resource-intensive. There was a dire need for a SaaS (Service as a Software) model which could offer companies flexible and scalable alternatives. The potential benefits of this shift were massive. SaaS removed the need to install software on local machines and allowed users to access it through the cloud. The software providers took care of hosting, updates, and maintenance. This change made software more affordable, easier to use, and more accessible.
In this blog, we will learn what is Service as a Software, what is software as a service, the differences between them and how this shift changed everything.
What is Service as a Software (SaaS)?
Service as Software shift is a concept of delivering traditional services (like customer support, consulting, or marketing) through a software platform. It often utilizes automation, AI, or machine learning to mimic human interaction. In this model, the focus shifts from providing a tool to offering a service through software. In this, technology is automated and service is improved. Thus, SaaS gives users a software tool to use, Service as Software which automates human services and delivers them as a digital experience.
What is Software as a Service (SaaS)?
SaaS (Software as a Service) refers to cloud-based software applications that are provided to users on a subscription basis. These apps include CRM tools, project management software and communication platforms. These tools are designed for users to perform specific tasks without worrying about installation, maintenance, or updates. According to Forbes, in software, companies provide tools like QuickBooks, but customers handle the outcomes. In the services business, however, the company takes responsibility for delivering results, such as AI-powered tax services. This shift creates a $4.6 trillion opportunity, as the global services market is much larger than the software market.
Need For Service as a Software And Challenges of SaaS

The main difference between Software as a Service (SaaS) and Service as a Software (SaaS) lies in what is being delivered to the user. SaaS provides cloud-based software tools to users that help them perform tasks. However, Service as software automates human services and delivers them through a software platform. This shift created more automated, and user-friendly experiences. Here are some challenges of software as a service that gave rise to service as a software:
Challenges of Software as a Service (SaaS):
Limited Responsibility for Outcomes:
One of the key challenges of the SaaS model is that companies provide the tools, but users are responsible for achieving the desired results. For example, with Salesforce. Users need to learn the software and make strategic decisions based on the data. For non-tech-savvy users, this could pose challenges to utilizing the full potential of the tool which causes inefficiencies and missed opportunities.
Customization and Complexity:
Many SaaS solutions are a “one-size-fits-all” approach. Still, they do not address the unique needs of every user or organization. However, some platforms allow for integrations and customizations. These integrations are complex, costly, and time-consuming to implement. That is why companies need to hire additional experts or consultants to tailor the software to their business needs. Nevertheless, with advancements in SaaS solutions, it is more difficult to maintain compatibility with other systems and ensuring that updates don’t break critical workflows can also pose challenges.
User Dependency and Learning Curve:
SaaS tools are generally user-friendly, but still, they require some degree of learning and adaptation. In addition, businesses need to dedicate time and resources to training staff or onboarding new users. This creates a barrier for businesses as they become dependent on user expertise. Mainly small businesses are affected because they have limited IT resources. Moreover, there is a high chance of failure as without proper training users cannot operate which impacts productivity and return on investment (ROI).
The Need for Service as a Software (SaaS)
In the above section, you read all the limitations of traditional Service as a software. That is why, the software industry is increasingly moving toward Service as a Software. According to SNS Insider Research, The Software as a Service (SaaS) Market size is expected to reach USD 1057.8 billion by 2032, with a growing CAGR of 13.62% in 2024-2032. This shift has changed the role of the user in achieving outcomes. It does not only provide the tool for users to operate but it also automates services and integrates them into a software platform. This way, companies can also take the responsibility of delivering the desired outcome. Also, they do not need to rely on users to navigate and operate the tools.
For example: QuickBooks can manage taxes. Instead of using this, the Service as a Software model provides fully automated tax services through an AI-powered accountant. This AI accountant can handle everything from tax preparation to filing. The user simply interacts with the software, and the system takes care of the rest. As a result, it ensures a seamless, hands-off experience. Therefore, this model shifts the focus from providing a tool to delivering a complete service, where the software handles the complexity of achieving the desired result.
Benefits of Service As a Software
Service as a Software automates services and cuts the need for users to manage and execute tasks. The software itself becomes responsible for ensuring that the right outcomes are achieved. Here are the benefits of Service as a Software over traditional SaaS models including :
Efficiency and Convenience:
Businesses and consumers can access fully automated services. It reduces the time and effort required to achieve specific outcomes. The backend technologies are AI and machine learning algorithms. These technologies can help perform tasks faster and more accurately than humans. As a result, it enables users to focus on higher-level decision-making rather than manual execution.
Scalability:
Traditional SaaS requires significant resources for customization or scaling. However, It can easily scale to meet the needs of larger or growing businesses. Automation can handle increased demand without requiring additional staff or infrastructure. As a result, it can lead to lower operational costs and greater flexibility.
Access to Advanced Technology:
Companies that adopt Service as a Software can leverage AI technologies without having to build them in-house. As a result, it allows even small companies to access powerful tools that were previously available only to large enterprises. Thus, it levels the playing field.
Reduced Dependency on Users:
Saas is automated and managed by the provider. In this, users do not need to be an expert in the underlying technology. As a result, it reduces the learning curve and makes the service more accessible to non-technical users.
Why Service as a Software Changes the Game of Businesses?
Service-as-Software changes the way businesses operate by embedding AI into workflows. It allows companies to streamline processes, reduce costs, and boost productivity. Traditionally, in Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) where users are responsible for leveraging tools to achieve outcomes. However, Service-as-Software takes on the responsibility of delivering results. Here’s how this shift is revolutionizing the business landscape:
1. AI Automation of Routine Tasks
Service-as-Software has the underlying technology of AI agents. These AI assistants automate repetitive tasks like customer support and inventory management. As a result, it frees up human employees for higher-value work. It boosts efficiency, improves quality, and delivers consistent results with fewer resources.
2. Scalability and Consistency in Performance
Training AI workers is straightforward and consistent compared to managing large human teams. These AI-driven services allow organizations to scale quickly and efficiently. AI workers are easier to train and update. They align with business goals in real time. As a result, it ensures high performance, even with increased workloads, while maintaining consistent quality across operations.
3. Streamlined Oversight and Quality Control
AI agents are monitored centrally. That is why, they can ensure performance standards are met. Unlike human workers, they can be quickly updated or retrained, reducing management complexity, lowering costs, and maintaining consistent results.
4. Connecting Systems-of-Record to Systems-of-Work
For AI workers to be effective, they need access to real-time, dynamic data across systems. Service-as-software is ideal for them. They get integrated in real-time data from Systems-of-Record and Systems-of-Work. It enables AI agents to make informed decisions. As a result, the integration helps AI optimize workflows, reduce errors, and ensure consistent results across operations.
5. Monetizing Service-as-Software: Outcome-Based Models
Service-as-Software shifts businesses from subscription-based pricing to outcome-based pricing. In this model, companies pay for the value AI agents deliver like tasks completed or outcomes achieved. This model aligns costs with results, maximizing ROI and ensuring investments are tied to performance.
6. AI Workforce Management
Companies have started adopting Service-as-Software. AI agents become crucial in this model. An AI workforce management system tracks performance to help meet goals and stay aligned with business objectives. Thus the system monitors key metrics like task completion and efficiency. The outcome is improved AI performance much like traditional HR systems manage human workers.
A SaaS Evolution, Not Extinction
Optimus Fox is a pioneer in AI development services and Saas provider. Their team strives to deliver comprehensive solutions to enterprises and businesses using automation. Do you know, that enterprise leaders who have spent decades using software to fuel their companies’ growth? And software has become the backbone of the modern technical economy. Ten years ago there were only 15 SaaS or software unicorns. Now, there are 416 of them. According to Forbes, the total public market cap of enterprise software companies exceeds $1 trillion. Optimus Fox provides AI development services that seamlessly integrate with SaaS platforms. We strive to empower businesses with efficiencies and success.
Conclusion
Service as software has transformed the business landscape and enabled organizations to automate traditionally human-driven services, improving efficiency, scalability, and consistency. AI in business workflows can help companies streamline operations, achieve higher performance and reduce complexity. It has outcome-based pricing that can help businesses to maximize ROI by paying for results. The SaaS market grows rapidly by offering scalable solutions that bring digital transformation. The SaaS market, valued at $195 billion in 2023, is expected to reach $245 billion by year







 Chat with us
Chat with us